Core Web Vitals: Learn How to Improve for Better SEO [2024]
It is a well-known fact that users prefer websites with exceptional page experiences.
Google has a long-standing reputation for prioritising the best possible user experience (UX). In recent years, the company has introduced further criteria to its search engine ranking algorithms, including website performance and mobile compatibility, to guarantee that users consistently receive the best experience when using Google to search for information online.
Table of Contents
What Are Core Web Vitals?
According to Google:
“Core Web Vitals is a set of real-world, user-centred metrics that quantify key aspects of the user experience. They measure dimensions of web usability such as load time, interactivity, and the stability of content as it loads (so you don’t accidentally tap that button when it shifts under your finger – how annoying!).”
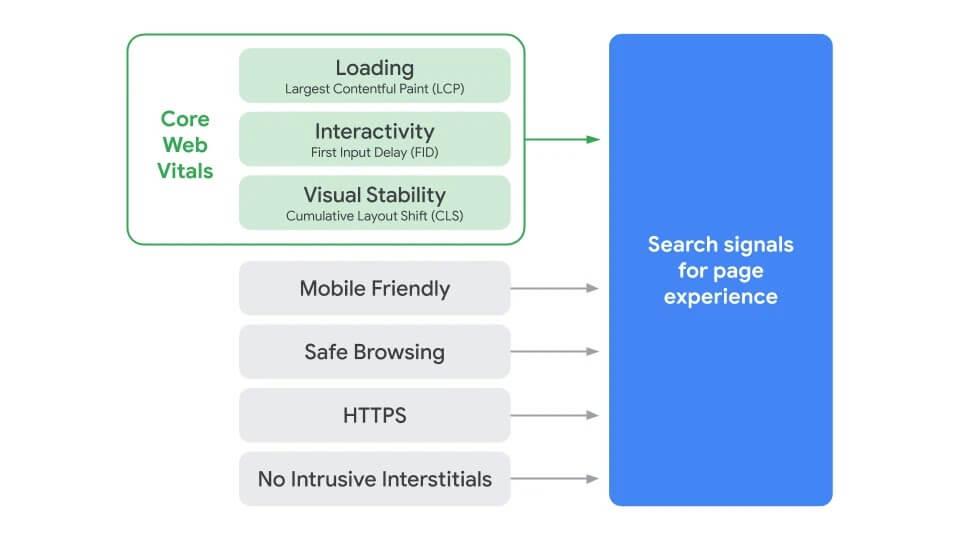
Web Vitals is an initiative by Google aimed at identifying and offering a unified guide to the quality signals that are critical to delivering an exceptional user experience on the web.
Core Web Vitals is a subset of the Web Vitals metrics that is relevant to all web pages. These metrics focus on speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. Google aims to assist website owners in measuring user experience on the web and creating a superior online experience for their users.
When Did Core Web Vitals Roll Out?
In May 2020, Google announced that the search engine would incorporate Core Web Vitals as a fundamental evaluation for the page experience. The new page experience signals merge Core Web Vitals with the search engine’s existing signals, including mobile-friendliness, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitial guidelines.
Starting from May 2021, Google began using page experience signals in its mobile ranking, with the rollout being completed by the end of March 2022, including the use of them in desktop ranking.
If you’re unsure where to begin, don’t worry! This article will guide you through the basics of enhancing your Google Core Web Vitals for SEO. We’ll also provide you with some useful tools and resources to get started. So let’s get going!
Are Core Web Vitals Important For Seo?
As a seasoned SEO agency, we are often asked about the significance of Google Core Web Vitals in search engine ranking. Core Web Vitals are essential for website optimisation and are among the numerous factors that Google takes into account when ranking a website. Optimising these elements can increase your website’s ranking and enhance your online visibility.
However, there are over 200 ranking factors, many of which have limited weight. The impact of Core Web Vitals on SEO can be significant for websites with poor page experience, but it will not affect websites with good user experience. This is because Google still places priority on other ranking factors, such as the quality of content, site authority, and backlinks when determining website rankings.
We will introduce a new signal that combines Core Web Vitals with our existing signals for page experience to provide a holistic picture of the quality of a user’s experience on a web page.
As part of this update, we’ll also incorporate the page experience metrics into our ranking criteria for the Top Stories feature in Search on mobile, and remove the AMP requirement from Top Stories eligibility.
Google: Evaluating page experience for a better web
Google Core Web Vitals
The metrics used in the Core Web Vital signal will change over time, but as of March 2024, they include:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
The LCP metric helps users understand the time they need to wait for the main content of the page to load, enabling them to determine whether the page is worth their time.
For an optimal user experience, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of the page beginning to load.

Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
The CLS metric calculates visual stability and determines the amount of sudden design change in the visible content of the page. A low CLS helps create a satisfying experience for users.
For an optimal user experience, pages should maintain a CLS of less than 0.1.

Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
The Interaction to Next Paint (INP) metric gauges a webpage’s responsiveness by measuring the time from when a user initiates an interaction (such as clicking, tapping, or typing) until the next frame is painted, providing visual feedback.
It replaces the First Input Delay (FID) metric, offering a more comprehensive assessment of responsiveness by considering all interactions, not just the first one.
For an optimal user experience, pages should have an INP of less than 200 milliseconds.

How To Measure Core Web Vitals For My Website
Google provides several popular tools for web developers that support the measurement of Core Web Vitals, enabling you to conveniently identify and resolve user experience issues. These include Lighthouse, PageSpeed Insights, Chrome DevTools, Search Console, web.dev’s measure tool, the Web Vitals Chrome extension and a Chrome UX Report API.
Using the Google Measure tool, you can track and retain records of your page’s performance history.
Learn more about Google’s tools to analyse and improve the performance of your website.
Workflow To Improve Your User Experience With Core Web Vitals
If you’re looking to improve your website’s performance, Google has some recommendations for you. To optimise your website, follow these steps:
- Check the Core Web Vitals report in your Google Search Console to identify which pages require improvement.
- Use Google PageSpeed Insights (PSI) to examine the Largest Contentful Paint, Total Blocking Time (which correlates with INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift metrics for each page.
- Use the Lighthouse dev tool to measure Core Web Vitals and receive actionable guidance on what to improve. You can access Lighthouse by opening your Chrome browser and selecting Developer Tools.
- Run a performance report using Lighthouse.
- If you’d like real-time monitoring, install the Web Vitals Chrome extension to get a live view of key metrics.
- Deploy your changes and use PSI to analyse the improvements, then confirm better metrics are reported by the Google Search Console.
Read more about this workflow as recommended by Google.
Optimise Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
To optimise your LCP, you can consider the following key factors:
- Server: Choose a hosting provider that offers a fast response time, such as Temok. They offer a free migration, fast hosting infrastructure, and effective caching mechanisms, as well as a Content Delivery Network (CDN) via Cloudflare. This can help ensure that your website loads quickly for visitors. Temok also provides a free SSL certificate and a free Web Application Firewall (WAF) to keep your website secure.
- Caching: Implementing a caching mechanism on your website can help to serve content from its cached version, reducing the number of requests to the database server. Consider using the Autoptimize plugin for WordPress, which helps to compress and optimise assets.
- Front-end Code: Minimise and defer non-critical CSS and JS files. If you are using a commercial theme, it should already implement these best practices. If you are creating a custom theme, ensure you follow WordPress’ recommended practices.
- Prefetch and preconnect: If your website is connecting to 3rd party domains, you can improve your web performance metrics if you place dns-prefectch and preconnect directives in the head element of your website.
- Content: Make sure the content above the fold is minimal and optimised for your key pages. Try to put your large elements, such as embeds, videos, and image galleries below the fold on your key pages.
- Images: Optimise images to the correct format, size and resolution, and use an image optimisation tool if necessary. Consider using an image CDN, such as CloudImage, which can help improve the performance of your website by delivering images faster, and using modern image formats.
> See also: 10 reasons to use Cloudflare on your website
Optimise Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
To reduce CLS, consider the following key elements:
- Adding width and height attributes to images and video elements.
- Addressing dynamic placeholder settings for third-party ads, by predefining the ad slot area or placing them further down the page to limit content shifting.
- Reviewing embeddable widgets and iframes that may cause content shifting during loading, and defining the height to minimize the shift.
- Using the preload attribute for custom web fonts (Google fonts or others) to improve performance and reduce CLS.
Optimise Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
To reduce the Interaction to Next Paint (INP), consider the following steps:
- Split large JavaScript files into smaller parts, and only load the necessary ones for the specific page.
- Minimise the size and compress the JavaScript files.
- Delay the loading of non-priority JavaScript files until after the main content has loaded.
- Check the third-party scripts that you are using and make sure they are being served from a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and are minimised.
- Consider the third-party widgets that you are using, such as social media widgets, and aim to use as few as possible to reduce the impact on the FID.
Are You Having Difficulties With Google’s Core Web Vitals?
We’re here to help you!
If you’ve been struggling to enhance your website’s Core Web Vitals, you don’t have to worry anymore. Our team of search engine optimisation consultants is ready to assist you. Please feel free to contact us for support.

Our commitment to excellence is underscored by our recognition as a Top Technical SEO Company in London for 2024.
Managing Partner at Agile Digital Agency, Juan brings over two decades of digital expertise to the forefront. With a degree in Computer Sciences and a rich professional background spanning internationally acclaimed digital agencies, Juan is a seasoned digital professional. Specialising in web solutions, digital marketing, and innovation, he channels his skills to craft successful online solutions for clients.
Related
Articles


